Important
This use case description is a draft. It will be detailed and improved based on feedback from the community. If you have any feedback please contact us.
Test management with OpenProject
Purpose
This guide describes how OpenProject can be used for lightweight test management by modeling test plans, test cases, and test runs using built-in features such as work package types, workflows, custom fields and project templates. It enables teams to manage and execute tests within the same environment they already use for project and requirements tracking.
Scope and assumptions
This use case is intended for teams that:
- Already use OpenProject for project planning and requirements management
- Want to include manual or semi-automated testing workflows
- Need traceability between requirements, test cases, executions, and defects
This setup is not a replacement for full-scale test automation or advanced lab management tools, but rather a structured and integrated approach to test tracking.
Note
At OpenProject, automated testing is a key part of our development process. It helps us detect bugs early and avoid regressions, especially as the codebase grows. We use continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) to ensure that changes are tested and released quickly and reliably. You can see our automated test runs on GitHub Actions. In addition to automated tests, we also perform smoke tests and exploratory testing to cover areas that are harder to automate and to validate the overall user experience.
Structure and terminology
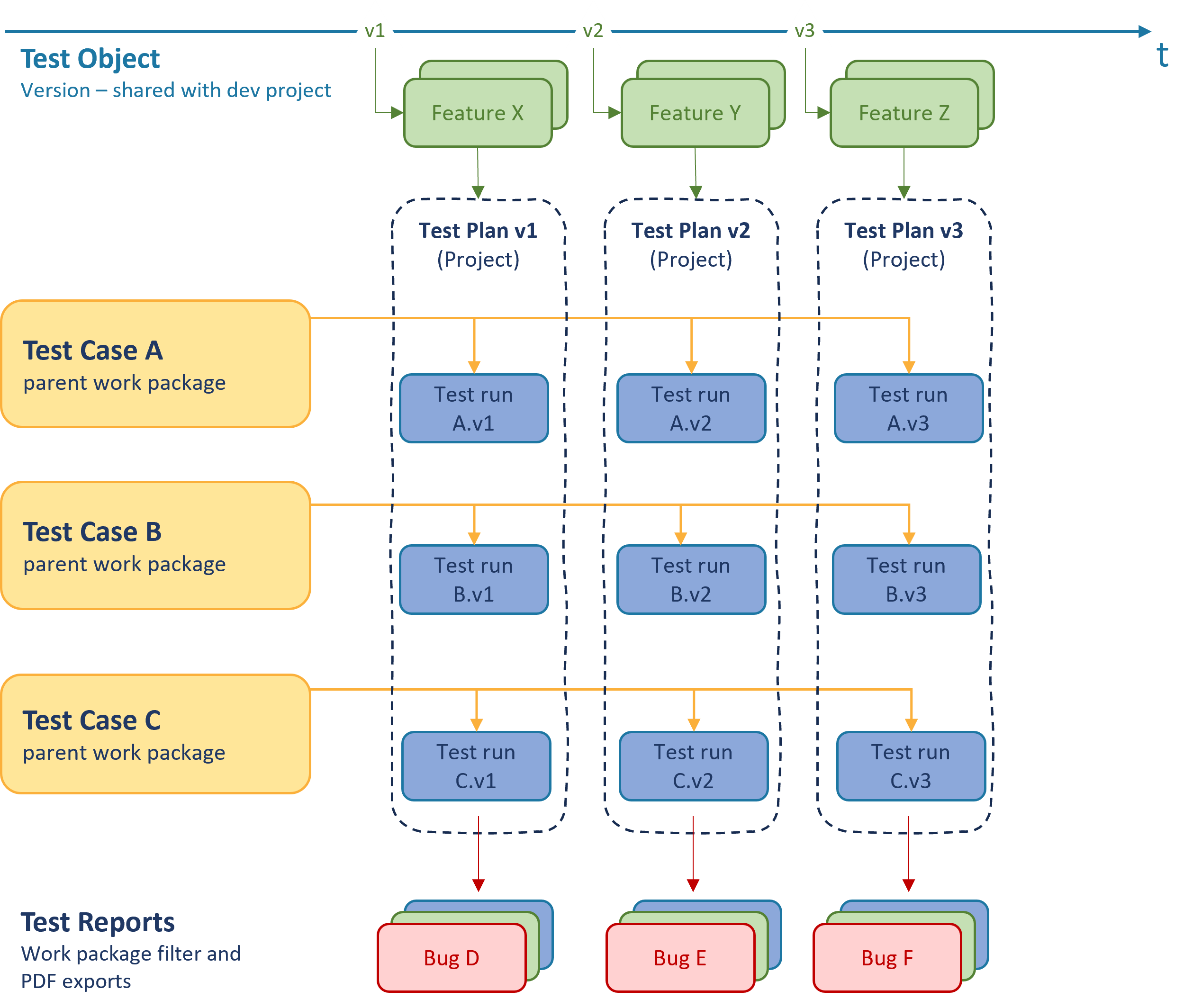
Core entities
| Concept | OpenProject entity |
|---|---|
| Requirements | Work package (e.g., type Feature or User Story) |
| Test case | Work package type Test Case |
| Test run | Work package type Test Run (child of test case) |
| Test plan | Project (created from a template) |
| Version under test | OpenProject Version field on test runs |
| Defect | Work package (e.g., type Bug) |
Relationships
- Each
FeatureorUser Storymay relate to one or moreTest Cases. - Each
Test Casedefines a reusable test specification. - Each
Test Casehas one or moreTest Runs(child work packages). - A
Test Runis specific to one software version. Test Plansare realized as individual projects per version, created from a reusable template.Bugscan be linked to failedTest Runs.
This structure supports traceability from requirements to execution and defect reporting.
1. Test preparation and execution
1.1 Creating a test plan (project)
A new test plan project is created based on a predefined template using the create project form.
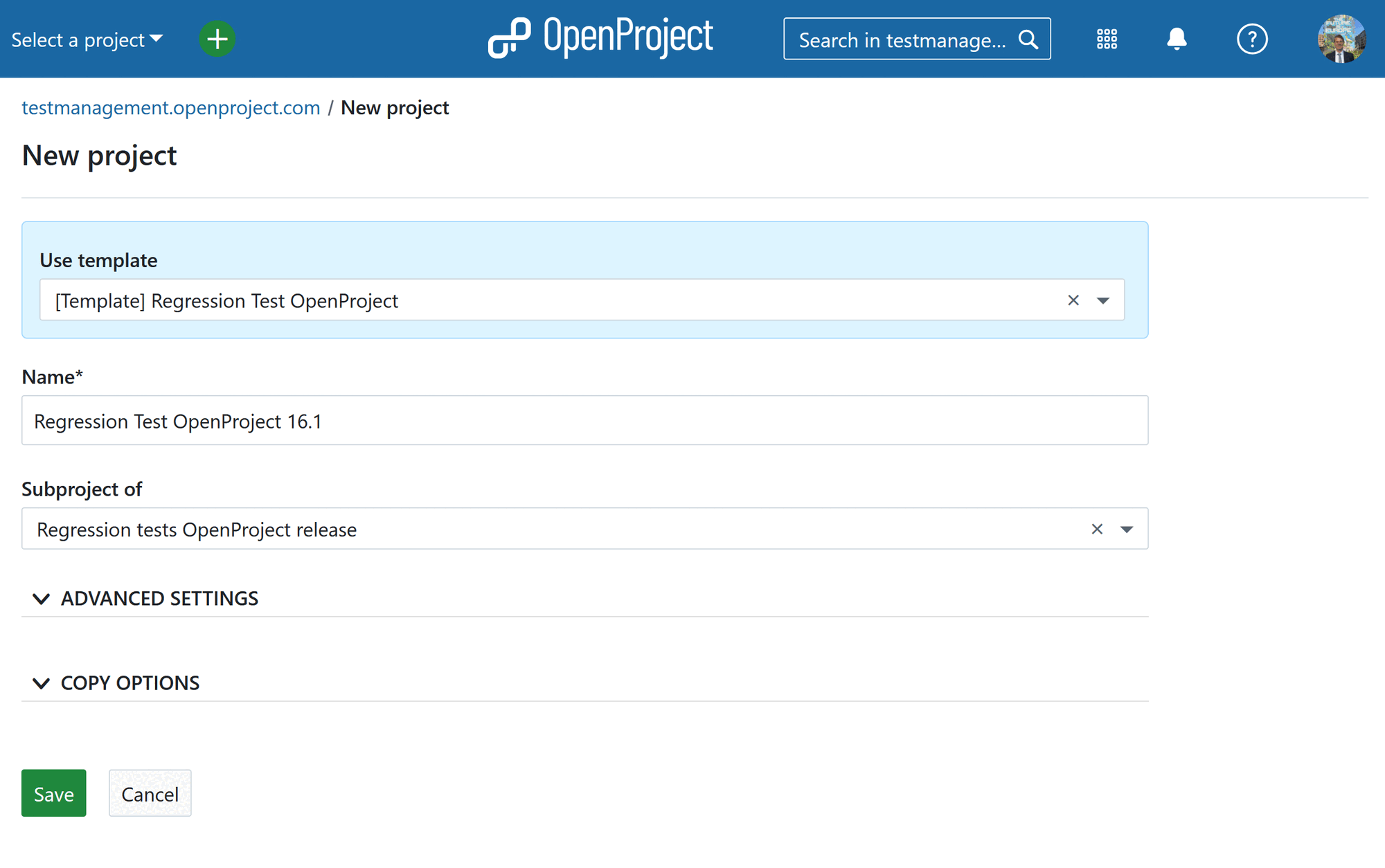
1.2 Adjusting the created test plan
In the next step the newly created test plan is adjusted by specifying the test object. The easiest way is to select all work packages (CMD + A) -> right click -> bulk edit.
- Version of the test object (version ideally shared from the development project)
- Tester
- Environment
For all test runs which are not planned the status should be adjusted to something like Not planned.
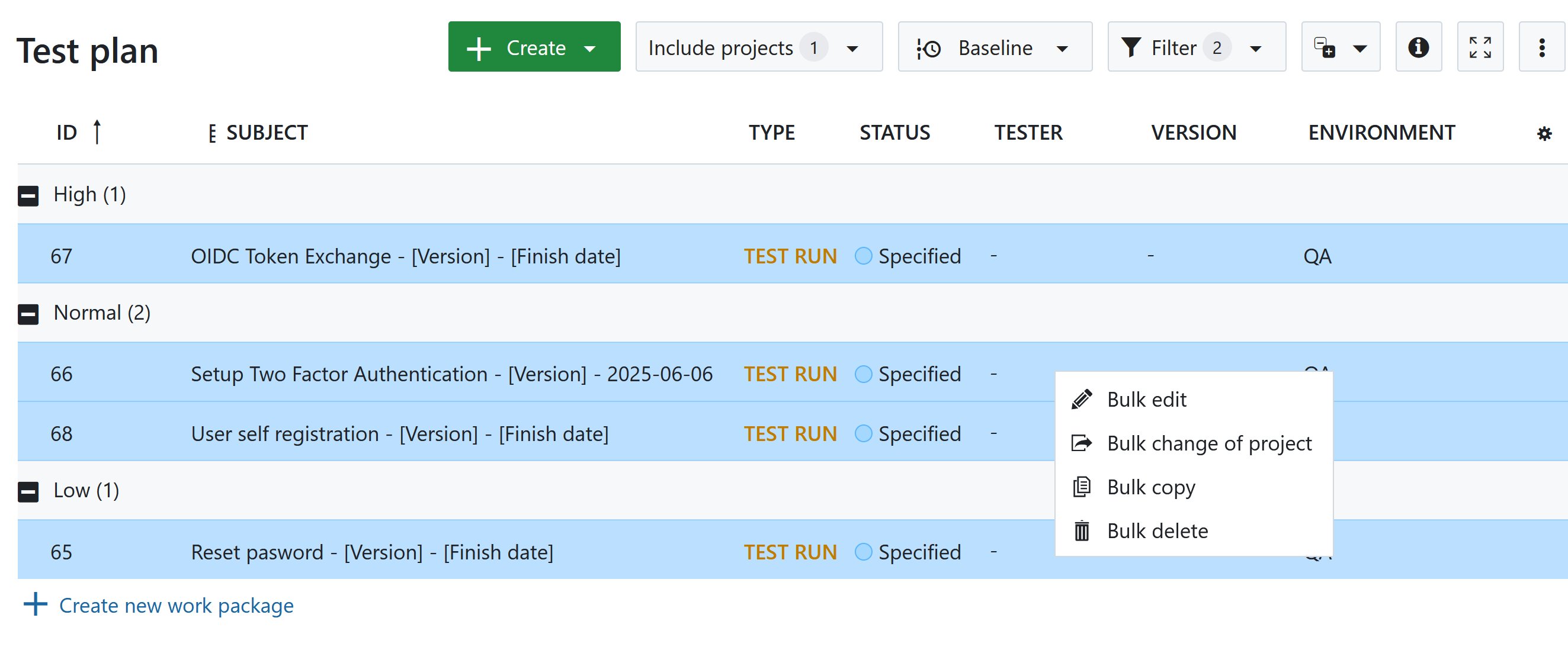
1.3 Test execution
- Testers open the project corresponding to the release version.
- Each test run is executed individually:
- Preconditions are verified
- Steps are performed
- Results are recorded
- Status is updated (e.g.,
Passed,Test failed,Blocked)
- If failures occur, related defects (bugs) are created and linked.
- Boards, filters, or hierarchy views are used to monitor test progress and coverage.
- The test result can be documented by creating a pdf report of the test status and results.
1.4 Progress tracking and reporting
As previously stated, agile boards (Kanban or Scrum) can help us track the test execution progress, i.e. visualize Test Runs by status (e.g., To Do , In Progress , Failed , Passed).
![]()
Comments and activity log (Activity tab) complement custom fields in the sense that they can also be used to record:
- Time and date of the execution
- Environment details (e.g., Browser, OS, Build version)
- Qualitative data and detailed explanations, as well as communication and collaboration between testers, developers and other stakeholders around a specific test case.
Activity tab is especially beneficial during the static testing phase. As a reminder, static testing is, among other things, verification of the test cases themselves (sort of testing of test case). Testers review the test cases/test runs searching for inconsistencies, errors, unclarity. Activity tab is a good place to discuss their findings, as well as track the complete and chronological history of a test.
Further tools can be used for reporting and metrics purposes with OpenProject:
- Saved filters: Create and save filters for “Failed Test Cases,” “Tests for Feature X,” “Tests due this week.”
- Export data: Apart from PDF, XLS and CSV are also supported.
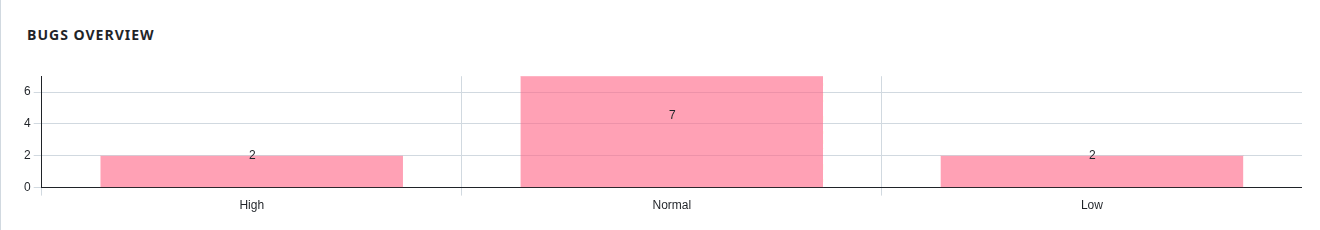
- Custom dashboards: On Overview page of your Test plan project, you can create graphs to:
- Count test cases by status (Passed, Failed, Blocked)
- Show tests assigned to each tester
- Track the number of open vs. closed defects, or simply have an overview of the bugs by priority.
1.5 Test case evolution: reusability and standardization
As test cases evolve, we need to track changes and reuse them across different cycles. There are several possibilities to achieve this:
- Duplicating work packages, copying projects, creating projects from template, moving work packages to another projects are all good methods for reusing test cases for new test cycles or for creating variations.
- Manual history can be tracked on the activity/comment log for any manual changes to test case steps.
- Naming conventions can be implemented (e.g., “TC-Login-ValidCredentials-v1.0”) to help manage variations.
To support consistency and standardization, OpenProject allows administrators to define automatically generated subjects for work packages. This feature enables the use of predefined patterns for naming, including for work package types such as Test Case and Test Run. As a result, newly created test cases and test runs automatically follow a consistent naming structure. This approach helps eliminate manual errors, improves searchability, and enhances filtering capabilities.
The subject pattern can incorporate dynamic attributes from the test case/test run itself (or its parent). In this example, Test run’s subject is derived from 2 fields: Parent's subject and Version.
Such subject is created upon save and is not manually editable.

Automatically generated subjects reduce manual effort and ensure that the name remains accurate and up-to-date if an attribute referenced in the subject pattern changes.
2. Test automation with GitHub and GitLab
2.1 Integration concept
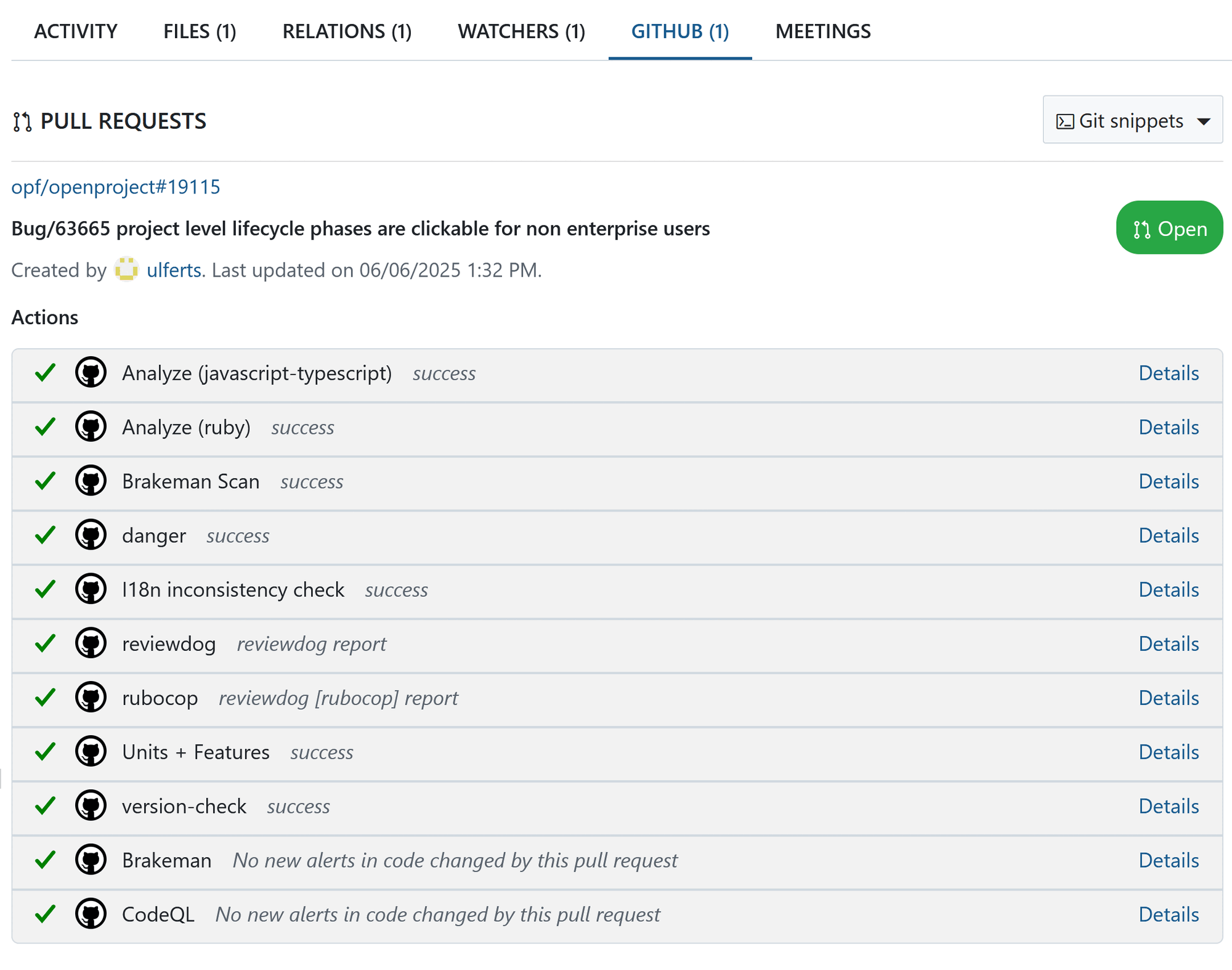
OpenProject enables seamless integration between software development and test automation workflows in GitHub and GitLab with planning and specification in OpenProject. Work packages can display information from GitHub pull requests and GitLab merge requests in a dedicated tab.
This tab lists all pull or merge requests linked to a work package, showing their status (e.g., Ready or Merged) as well as the current state (e.g., success or queued) of the actions configured to run for each request—whether in GitHub or GitLab. The results of these actions are also displayed within the tab.
The relationship between work packages and pull/merge requests is many-to-many: a single work package can be linked to multiple pull or merge requests, and a single pull or merge request can be associated with multiple work packages.
2.2 Benefits of the integration
Integrating GitHub and GitLab with OpenProject offers several advantages for software development teams:
- Enhanced traceability: By linking code changes directly to work packages, teams can easily trace the origin of each change, facilitating better understanding and accountability throughout the development process.
- Improved collaboration: Real-time visibility into the status of pull and merge requests fosters collaboration between developers, testers, and project managers, ensuring everyone stays informed and aligned.
- Streamlined workflows: Automated updates from GitHub and GitLab reduce manual tracking efforts, allowing teams to focus on development tasks and reducing the likelihood of oversight.
- Accelerated delivery: By integrating continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, teams can automate testing and deployment processes, leading to faster and more reliable software releases.
- Comprehensive reporting: Consolidated data from development and project management tools enables more comprehensive reporting and analytics, supporting informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
3. Configuration guidance
This section provides guidance on how to configure OpenProject for test management. It assumes familiarity with OpenProject administration features.
3.1 Configuration example: Test Cases (work package type)
The work package type Test case can be configured so it shows the relevant information:
- Test runs (related work packages table
children) - Tested features (related work packages
requires) - Priority
- Tested module (custom field of type
Hierarchy)
Here you find an example for a test case.
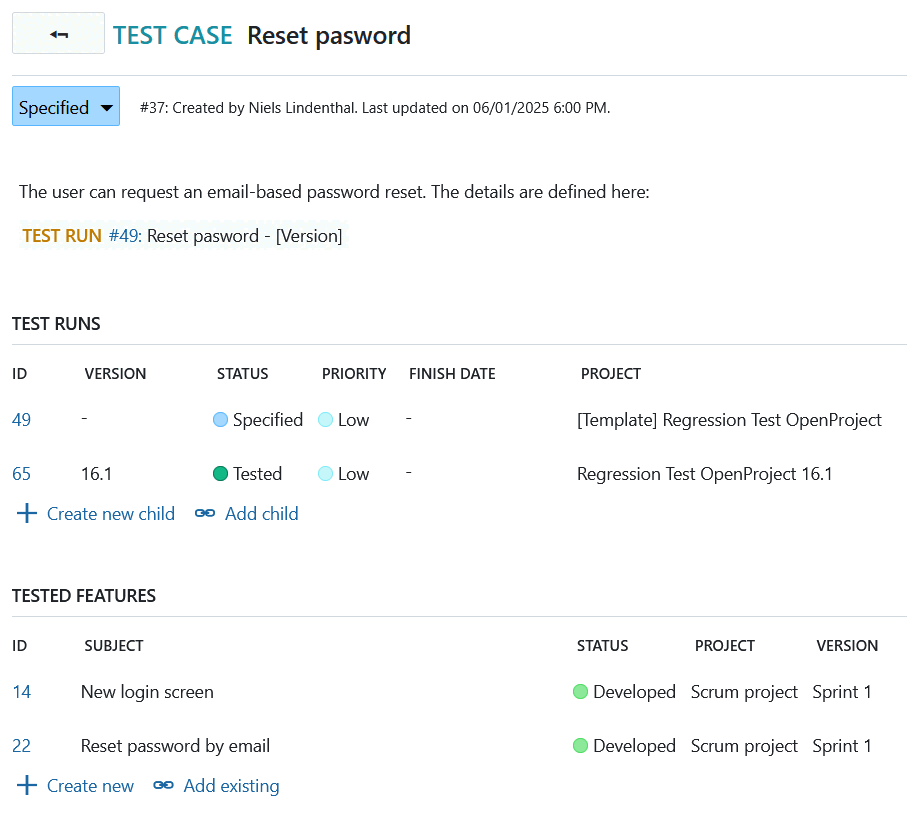
3.2 Configuration example: Test Run (work package type)
The work package type Test run can be configured so it shows the relevant information:
- Test specification including preconditions, execution steps and test results: Description field
- Tested features (related work packages
requires) - Priority
- Tester (custom field of type user)
- Identified bugs (related work packages
related to)
Here you find an example for a test run.
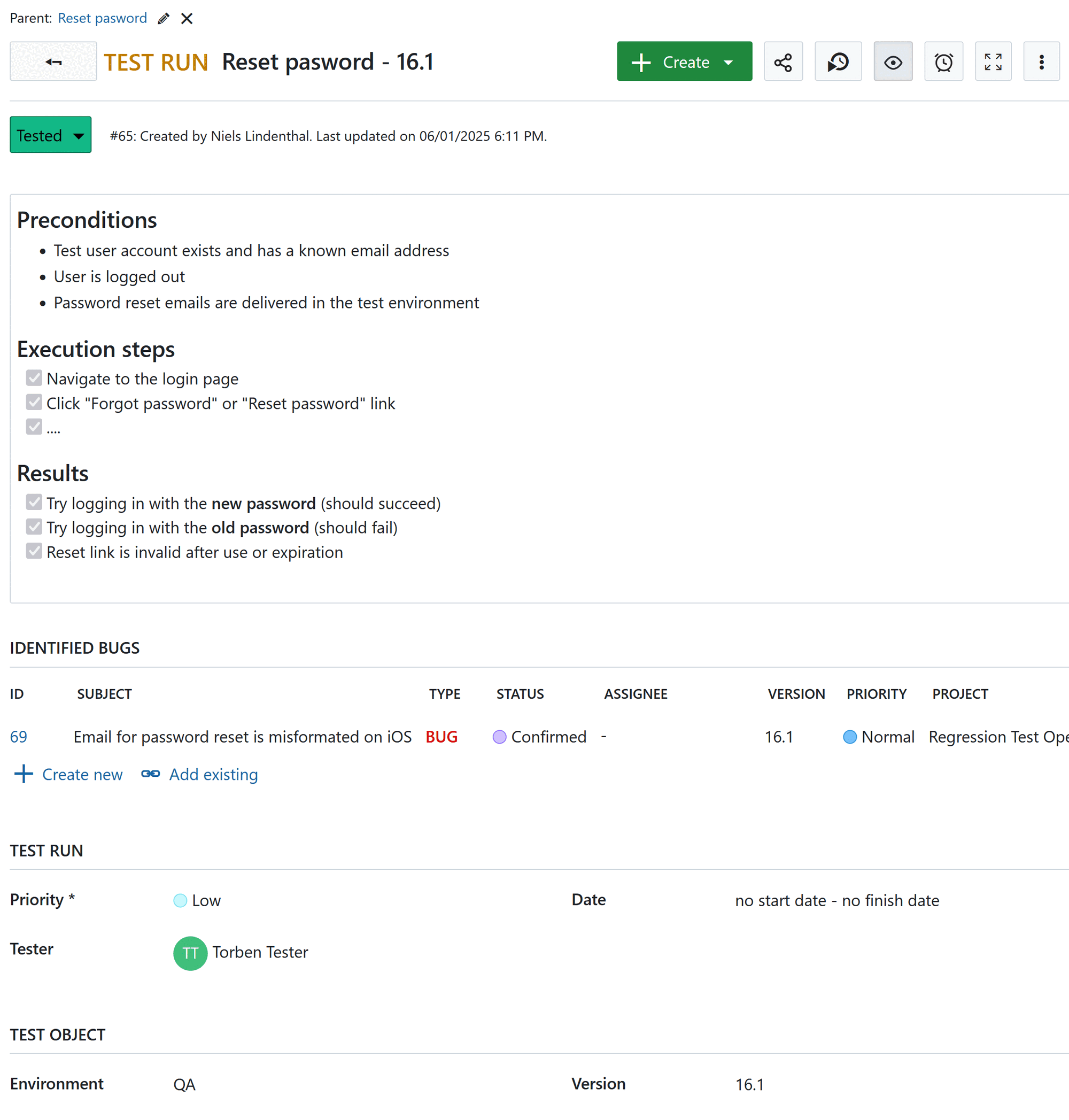
3.3 Roles and permissions
-
Define useful roles such as:
TesterTest Manager
-
Add permissions such as:
- Edit work packages
3.4 Custom fields
Define custom fields that describe the test object such as:
- Test environment (type
hierarchy) - Tester (custom field type
user)
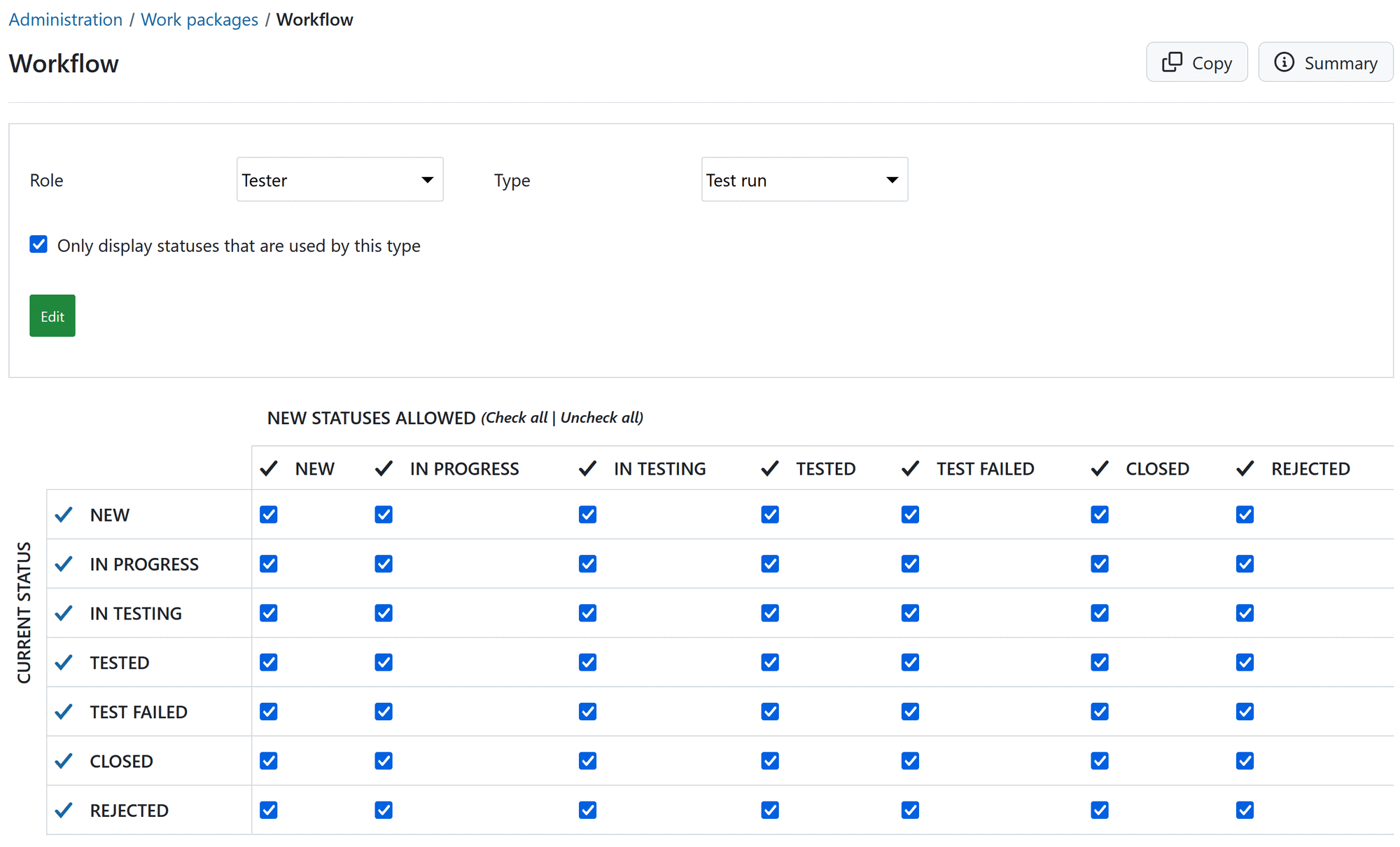
3.5 Workflow and statuses
- Define custom statuses such as:
New,In progressTest passedTest failed- …
- Create a simple workflow for test runs with allowed transitions
- Optionally restrict who can move a test run to
Test passed.