PRINCE2 with OpenProject
PRINCE2 project management with OpenProject
When managing complex projects, it is beneficial to use a project management methodology for guidance. PRINCE2 is one of the most popular and widely used methodologies available.
What is PRINCE2?
PRINCE2 (or Projects in Controlled Environments) offers a structured process for projects & provides recommendations for each project phase. It is one of the leading project management methodologies (next to PMBOK (from the Project Management Institute)) and used in over 150 countries.
Basic principles of PRINCE2
PRINCE2 provides a clear structure for projects and is based on 7 principles, 7 themes and 7 processes as described by PRINCE2.com.
7 Principles
PRINCE2 is build on seven principles which represent guiding obligations and good practices.
The 7 Principles are:
- Continued Business Justification: A project must make good business sense (justified use of time and resources, clear return on investment).
- Learn from Experience: Previous projects should be taken into account. Project teams use a lessons log for this purpose.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities: The decision makers in the project are clearly defined. Everyone in the project knows what they and others are doing.
- Manage by Stages: Difficult tasks are broken into manageable chunks, or management stages.
- Manage by Exception: The project board is only informed if there is or may be a problem. As long as the product is running well, there is not a lot intervention from managers
- Focus on Products: Everyone knows ahead of time what is expected of the product. Product requirements determine work activity.
- Tailor to the Environment: The PRINCE2 methodology can be tailored and scaled. Projects which are adjusted based on the actual needs perform better in general than projects which use PRINCE2 dogmatically.
7 Themes
In addition to these 7 Principles, there are 7 Themes which are addressed continually throughout the project. They provide guidance for how the project should be managed. They are set up at the beginning of the project and then monitored continually to keep the project on track:
- Business Case: This theme is used to determine if a project is worthwhile and achievable. It is related to the principle of Continued Business Justification.
- Organization: Project managers are required to keep a record every team member’s roles and responsibilities. It is related to the Define Roles and Responsibilities principle.
- Quality: At the beginning of the project the project manager defines what constitutes the quality of the projects. This is related to the Focus on Products principle.
- Plans: A plan is set up which describes how objectives are going to be achieved. It is focused on cost, quality, benefits, timescale and products.
- Risk: Uncertain events during the project are identified, assessed and controlled. They are recorded in a risk log. Positive risks are called opportunities, negative risks are called threats.
- Change: How to handle change requests and issues which arise during the project. Changes shouldn’t be avoided but they should be agreed on before they are executed.
- Progress: This principle is about tracking the project. This allows project managers to verify and control if they are performing according to the project plan.
7 Processes
To structure the step-wise progression through a project, there are 7 Processes. Every one of the steps is overseen by the project manager and approved by the project board:
- 1. Starting up a project
- Create a project mandate to answer logistical questions about the project. It covers the purpose of the project, who will carry it out and how to execute it.
- From the project mandate a project brief is derived, as well as lessons log and discussions with project members.
- A project team is assigned.
- 2. Initiating a project
- During this stage project manager determines what needs to be done to complete the project and outlines how the performance targets will be managed (cost, time, quality, benefits, risks, scope)
- 3. Directing a project
- This is an ongoing process covering the entire life time of the project.
- The project board manages activities such as initiation, stage boundaries, guidance, project closure.
- 4. Controlling a stage
- Project managers break the project into work packages / manageable activities and assigns them to the project members.
- The project manager oversees and reports the work package progress.
- 5. Managing product delivery
- This manages how the communication between the team and the project manager is controlled.
- The activities include accepting, executing and delivering work packages.
- 6. Managing stage boundaries
- The project manager and the board review every stage. The board decides whether to continue the project. The project manager records lessons learned with the team for the next stage.
- This process includes
- Planning the next stage
- Updating the project plan
- Updating the business case
- Reporting the stage end or producing an exception plan
- 7. Closing a project
- In the final process the project is closed. This includes decommissioning the project, identifying follow-on actions, preparing project evaluation and benefits reviews, freeing up leftover resources and handing over products to the customer
Implementing PRINCE2 with OpenProject
OpenProject supports the seven processes (as well as the principles and themes) laid out by the PRINCE2 methodology.
1. Starting up a project
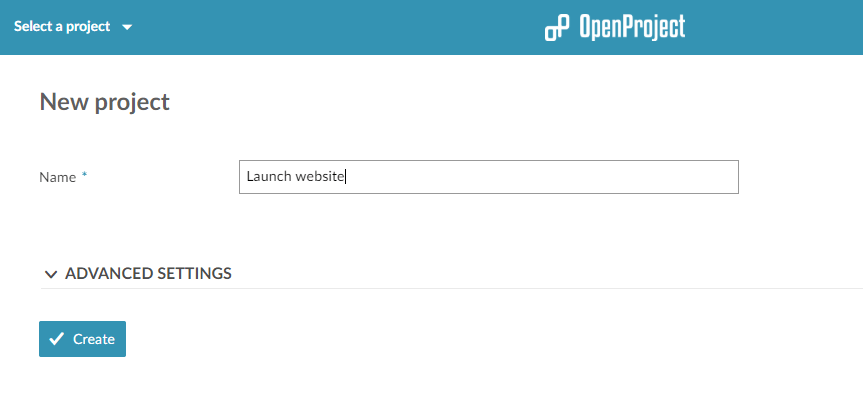
Starting up a project in OpenProject starts by creating a project.
Simply choose Select a project from the top left side and select + Project from the dropdown menu.
Next, provide a name and click on Create.
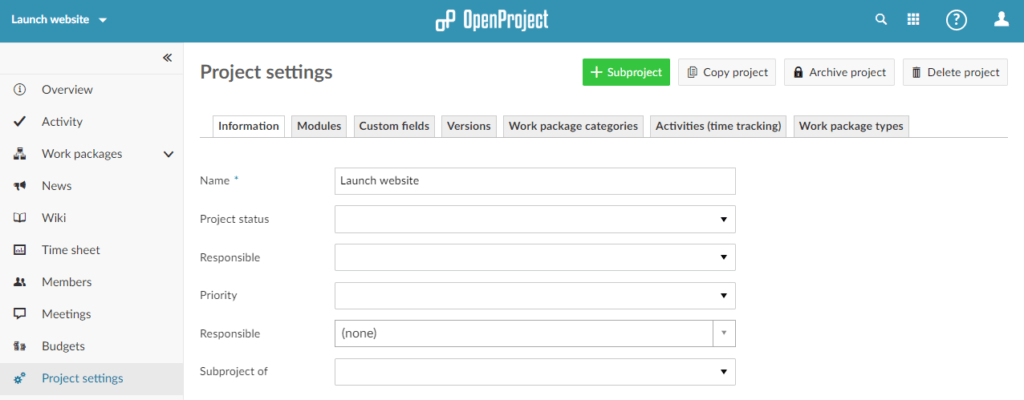
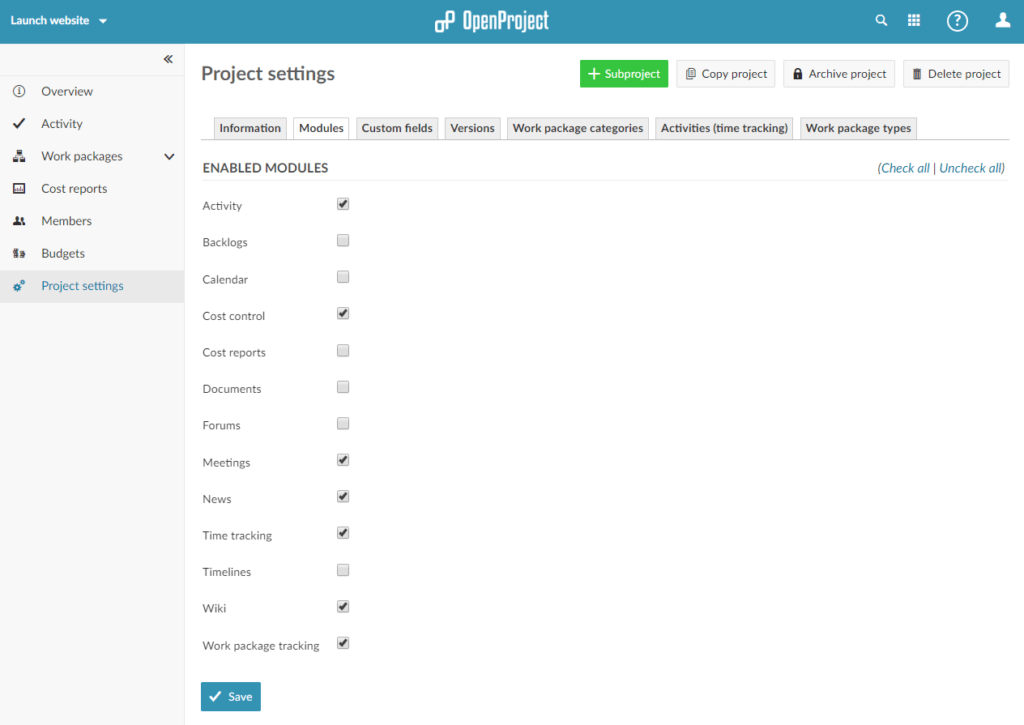
Within the project make sure that Wiki is displayed on the left side. If it is not shown, select Project settings and choose Wiki before clicking Save. Also make sure to activate Cost control and (optionally) Meetings, Forums and News.
Next, select Wiki from the side menu on the left side and use it to create the Project Mandate. Make sure to press the Save button at the end.
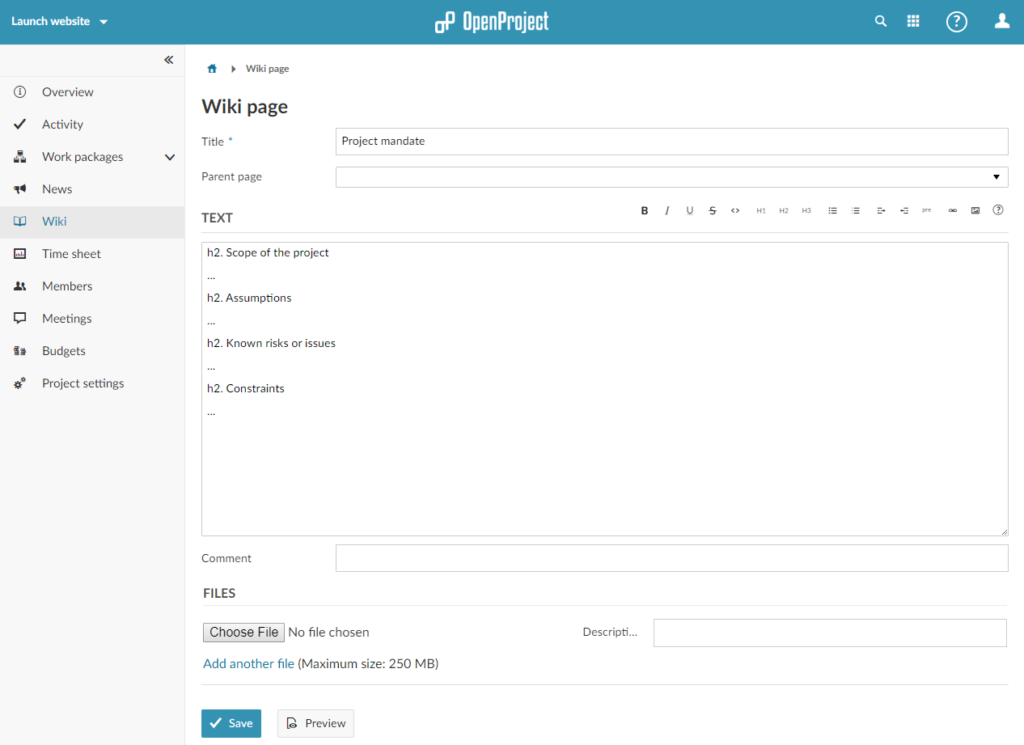
You can create the Lessons log as well by creating an additional Wiki page. Simply click on the green + Wiki button which is shown once you created the Project mandate.
Afterwards, select Members from the side menu to add the project members and assign them roles.
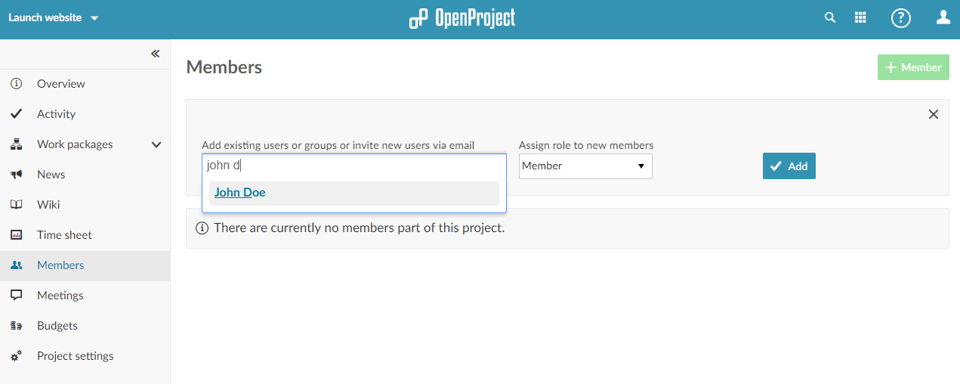
If the project members do not yet have an OpenProject account, you can create one for them in the administration (select your user avatar in the upper right side, select Administration and click on + User to create a new user.
You can also assign entire groups to add multiple project members at once. Simply select them instead of individual users.
2. Initiating a project
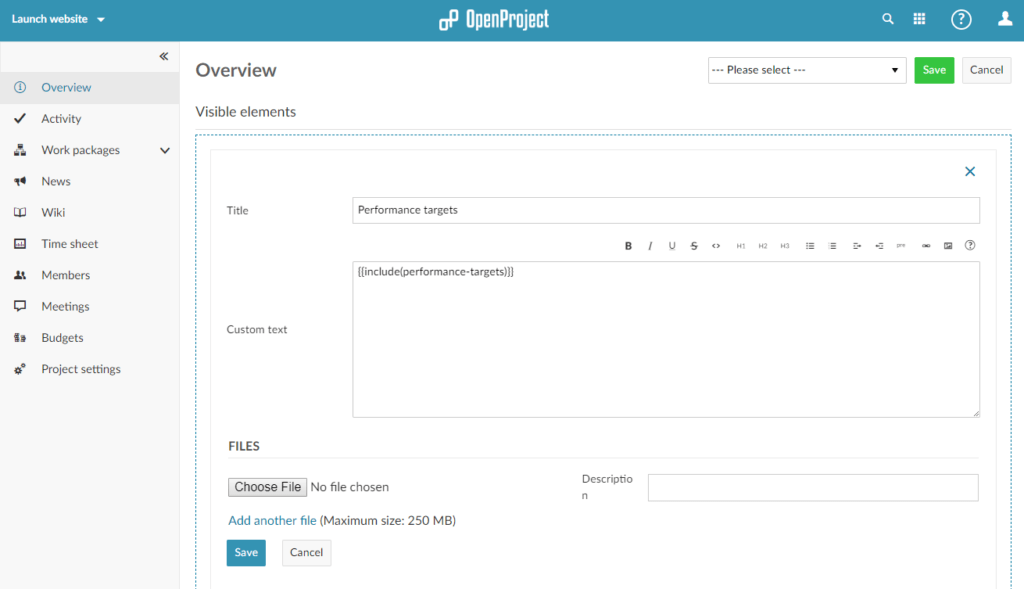
After setting up the project continue by documenting the performance targets in a wiki.
You can include the wiki in the project overview so that all project members can see the objectives right away. To do this, select Overview from the side menu, click on the gear icon and choose Add teaser … from the dropdown menu. Include the wiki page by using the following syntax: {{include(Wiki_name)}} (replace Wiki_name with the name of your wiki page).
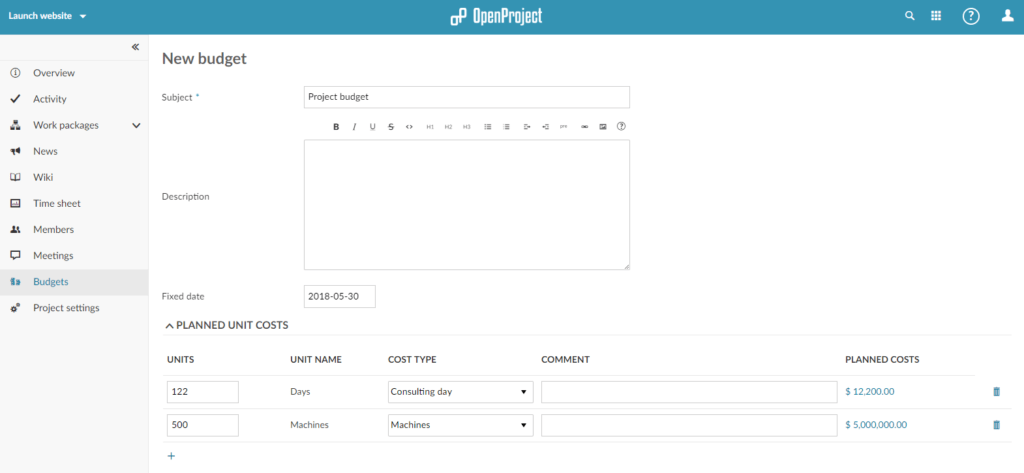
Continue by setting up a budget. Select Budgets from the left side menu, provide a name and assign the unit and labor cost.
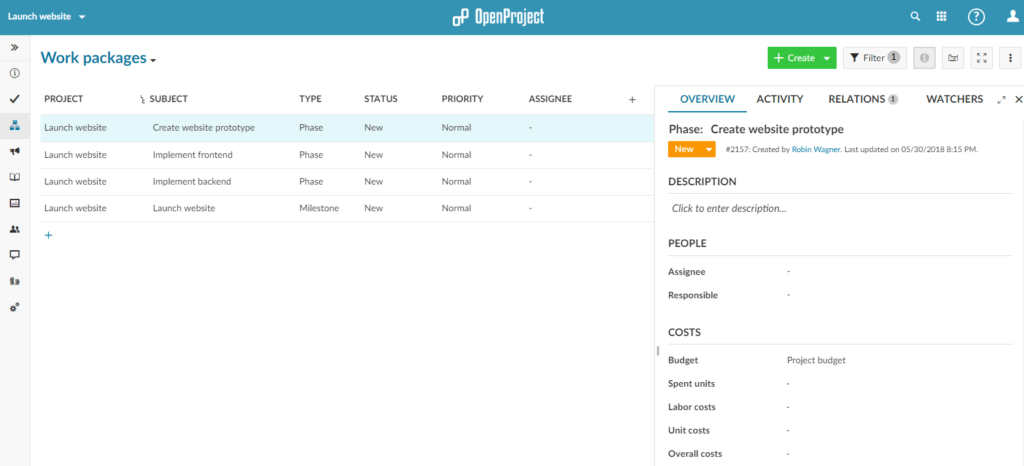
After creating the budget, navigate to the work package table and create the phases and milestones for the project. Do this by clicking on the little + icon below the work package table. You can assign the phases and milestones to the budget by opening the details view (click the info icon) and setting the Budget attribute in the Costs group to the budget you just created.
3. Directing a project
After setting up the phases and milestones continue by activating the Gantt and setting the start and due date of the phases and milestones. To do this, simply hover over the Gantt chart, hold your mouse key and drag to set the start and due date.
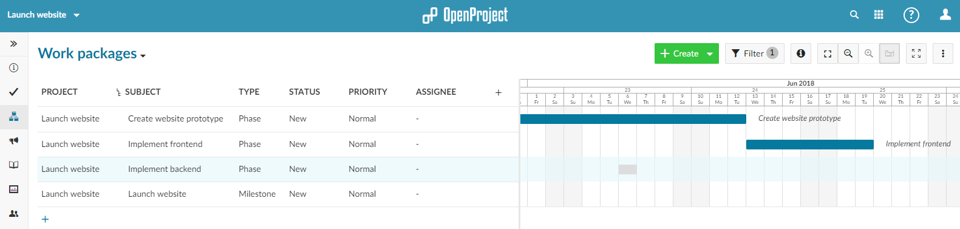
Continue by creating dependencies by right-clicking on a phase or milestone and selecting Add follower from the menu. Then, select the following phase or milestone. Repeat this for the different phases and milestones.
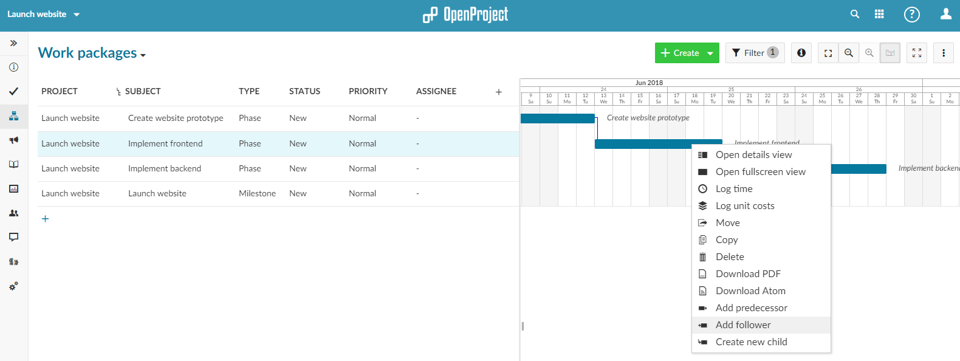
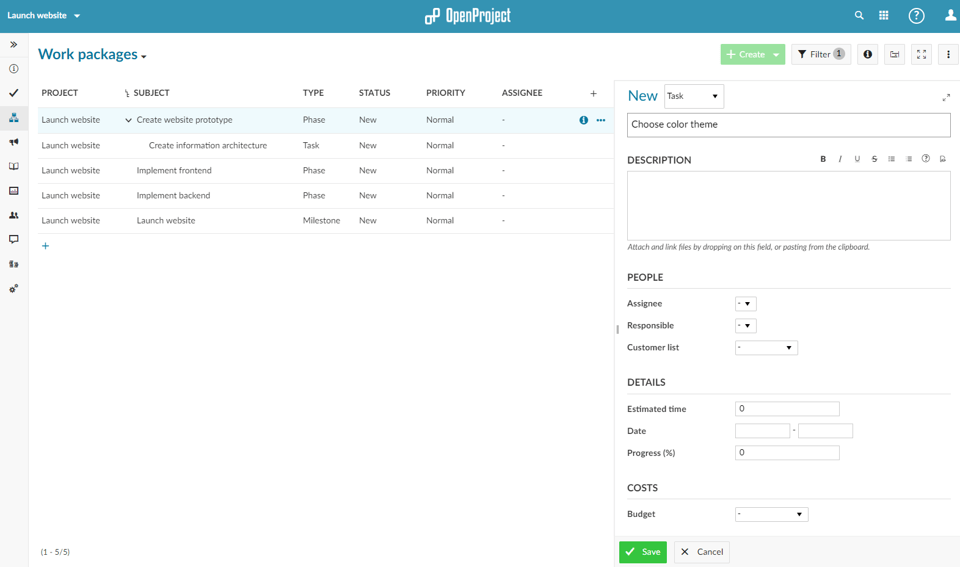
4. Controlling a stage
After setting up the initial phases and milestones continue by breaking the phases down into work packages. To do this, click on the three little dots next to a phase and select Create new child. Select type Task (or Work package if you created a separate type for this (see the user guide on how to create a new type)).
Add the column Estimated time to provide an effort estimate in hours. To do this click on the little + icon on the right side next to the existing columns and choose Estimated time from the available columns. Then, enter the time estimate by simply clicking on the respective cell and entering the time estimate in hours.
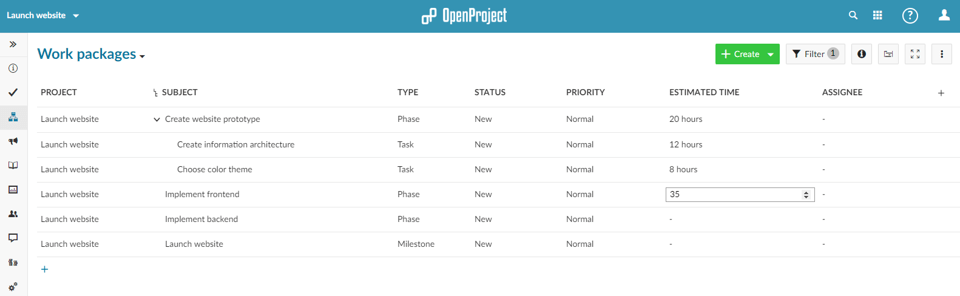
Afterwards, continue by assigning the work packages to the project members by clicking on the cells in the Assignee column.
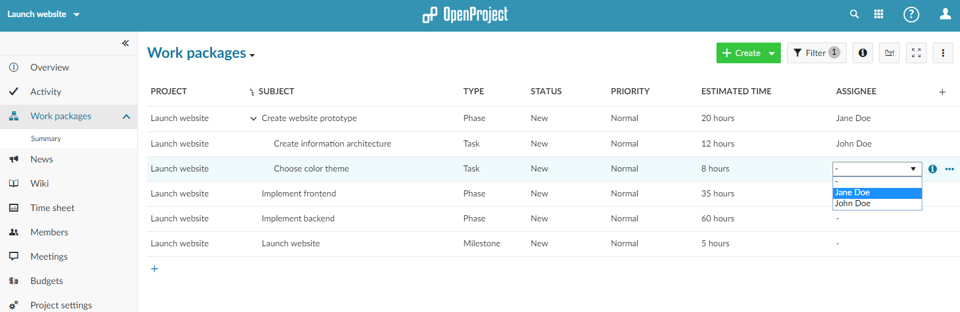
5. Managing product delivery
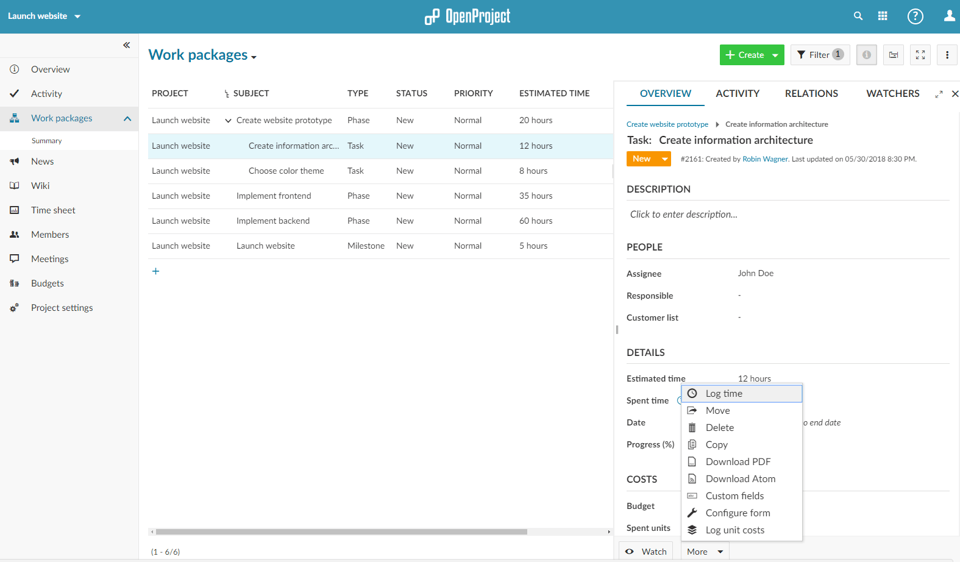
While working on the project, project members can log their time by opening the work package details view, selecting the More button and then the Log time entry.
To facilitate the communication within the project, OpenProject offers the forums, meetings and news module.
6. Managing stage boundaries
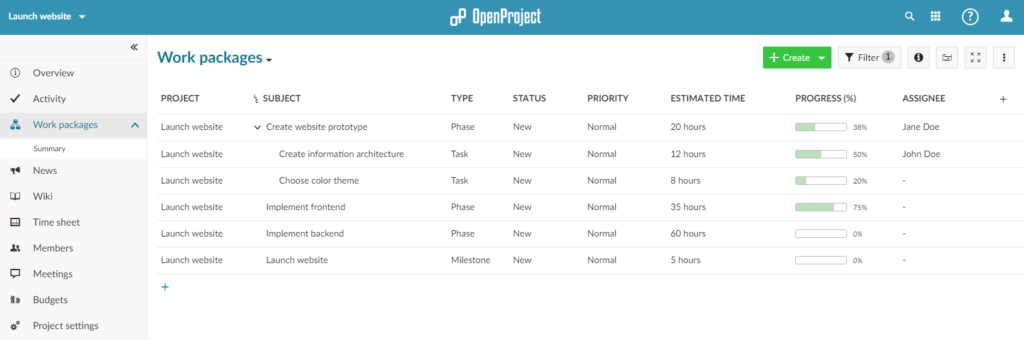
The progress of the phases is documented automatically in the Activity section of the phase. Additionally, the progress can be set directly.
For a better overview add the Progress column to the work package table.
During the duration of the project you can also easily update and reschedule the phases in order to reflect the current project status.
7. Closing the project
When all the tasks / work packages, phases and milestones and phases have been completed you can document the final project report in a wiki page.
As a last step you can archive the project by selecting Project settings and then Archive project.